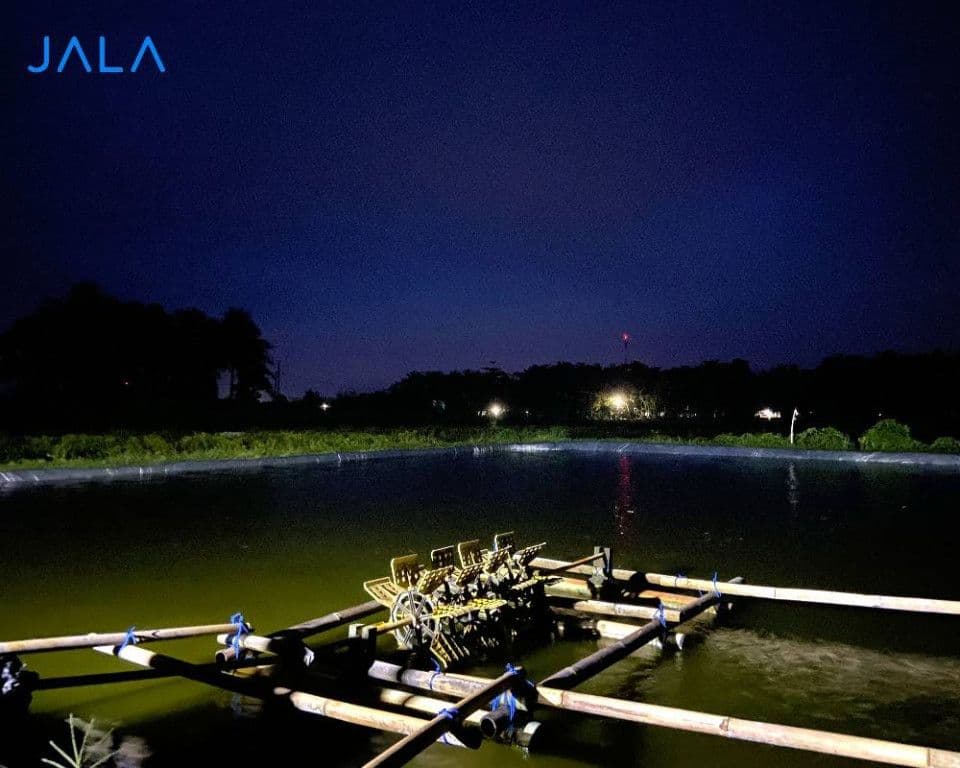
Moon phases affect the tides, seasonal changes, and circadian rhythm, which in turn affect the behavior of aquatic life. Moon phases are especially impactful towards fishery and marine life, including organisms in the sea, river, and mangrove ecosystems. Moon phase phenomenons have an indirect effect on the biological cycles of fish.
Moon phases impact natural phenomena on the earth, such as tides, due to the gravitational effect of the moon and sun as well as the earth’s rotation. This knowledge has been applied when it comes to catching fish. In fish cultivation, moon phases are known to affect the molting cycles of crustaceans, including shrimp.
Moon phases affect molting cycles
Molting cycles in vannamei shrimp is much attributed to moon phases. During the new moon, 80% of shrimp reach ecdysis stage (the process of shedding the exoskeleton). Vannamei shrimp usually experience molting at night during the full moon or high tides.
Molting is a periodic process experienced by shrimp as part of their growth. Since the exoskeleton does not grow with the shrimp’s body, the shrimp needs to ‘change its skin’. Molting can also occur due to stress in shrimp.
Molting cycles consist of molt, postmolt, intermolt, and premolt. The molt phase is the ecdysis process. The phase after ecdysis is called postmolt, where the exoskeleton is still soft and absorbing minerals. Afterward, mineralization occurs, which hardens the exoskeleton.
The intermolt or anecdysis phase is an inactive period and the longest in molting cycles. During this time, muscle regeneration occurs, as well as storage of energy for the next ecdysis. Premolt or proecdysis is a phase where somatic muscle atrophy occurs. During premolt, minerals from the exoskeleton are reabsorbed to form new exoskeleton as a preparation for ecdysis.
Electromagnetic radiation or gravitational pull from the moon is thought to trigger the release of neurohormones. In Scylla, the y-organ produces molting hormones or ecdysteroids in patterns that relate to moon phases.
The concentration and amount of ecdysteroids decrease during the new moon, and increase as the crescent moon phase begins. It reaches its peak during the half-moon. Another sharp decrease occurs during the full moon, causing ecdysis.
The relationship between moon phases and molting of vannamei shrimp in farms has not been discussed in depth. However, it can be adapted from research involving other cultivated crustaceans. Knowing the effect of moon phases on shrimp physiology can help in taking preventive measures for molting failure during the full moon.
Shrimp in the ecdysis and postmolt phase are highly sensitive towards the presence of vibrio bacteria, and more susceptible to bacterial infections due to vibrio during the new moon phase. During this time, shrimp is experiencing ecdysis or shedding of the exoskeleton.
Shrimp undergoing molting needs sufficient minerals and nutrients. Two of the most important minerals are calcium and magnesium, which helps them regenerate new exoskeleton quickly.
During molting, shrimp will fast and use up proteins in their body to form a new exoskeleton in a few hours. This process is highly risky and will make shrimp more vulnerable to changes in water quality, especially in maintaining osmotic pressure in their body. If this condition continues, osmotic shock may occur, where there is an excess of water absorption in the shrimp’s cells.
The partial decomposition of the exoskeleton that happens during molting easily stimulates other shrimp. Fluids containing amino acid compounds, enzymes, and other organic compounds increase the appetite of non-molting or post-molting shrimp, which may potentially result in cannibalism.
What steps should be taken in shrimp farms to anticipate different moon phases?
- Check shrimp molting phases regularly. Check and record them by sampling to predict when molting will occur in the farm. As an extra consideration, check the moon phase when checking.
- Maintain water quality, particularly salinity, to prevent drastic changes and minimize the risk of osmotic shock.
- Decrease feed amount depending on the phase. Feeding shrimp during molting helps to prevent overfeeding, which may negatively affect water quality and cause diseases. Attempt to give a sufficient amount to prevent cannibalism.
- During the full moon, molting may happen all together, causing mineral content to decrease quickly. Apply minerals such as calcium and phosphorus to speed up the process of forming new exoskeleton in shrimp.
- Minerals should be controlled to prevent problems. If mineral content decreases and the farm is experiencing high algal density, high and sudden mortality may occur, further worsening the conditions with the increase of organic materials, bacteria, and toxic gas.
- Maintaining pH is important to support molting. Experts suggest an ideal pH of 7.8-8.2 for molting. To keep pH stable, maintain an alkalinity of 100-120 mg/l.
- When shrimp enter the molting phase, they need twice the amount of oxygen than usual. Make sure there is sufficient DO supply to support the molting process.
Moon phases affect the tides
Scientifically, every living organism has biological cycles and responses towards changes in light and ambient temperature due to the moonlight at night. In fishing, this knowledge is used by fishermen to predict when fish are most active. Fishermen will easily find and catch fish during the new moon phase. A significant difference in terms of species diversity and number can be felt between different moon phases.
In shrimp cultivation, tides should be taken into account when constructing farms. Ideal shrimp farm locations are those with tide fluctuations of 2-3 meters. Knowing the tides in shrimp farming is important to determine:
- Pond base layout
- Primary/main channel base
- Secondary channel base
- Width and height of embankment and inlet and outlet channel dimensions
Tide considerations are required in the process of adding and removing water from the pond, which makes use of gravity to increase energy efficiency from the electricity or fuel for the water pump.
Moon phases affect the tides, which are the rising and falling of seawater due to gravity between the earth-moon-sun. Tides can be classified as:
Two high and low tides each day with roughly similar heights, occurring consecutively and regularly with a period of 24 hours and 50 minutes. Semi-diurnal tides occur along the equator.
One high and low tide each day with an average period of 12 hours and 24 minutes.
The difference in gravity of the earth, moon, and sun which affect one another due to the distance between them causes a variety of tides. The sun’s gravity has very little effect since it is a great distance away. The most significant effect comes from the moon’s gravity.
The new moon phase, which occurs when the moon and sun are in line with the earth, results in the highest and lowest tides. The relationship between moon phases and tides are shown in the following illustration.
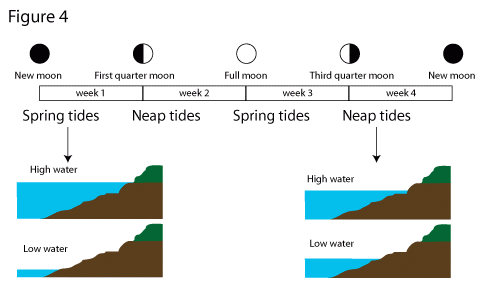
Water conditions, beach morphology, and complex water bathymetry determine tide patterns in different regions. Some regions with high tides include the seas in east Riau, the seas and estuaries between South Sumatra and Bangka, the seas and strait around Madura island, the coast of East Kalimantan, and the estuary in south Papua.
About moon phase
In definition, moon phases are the changes in moon shape as seen from the earth. There are at least four main phases: new moon, first quarter, full moon, and third quarter. The time taken to reach another new moon is 29 days 12 hours 44 minutes and 3 seconds.
The moon orbits around the earth in the shape of an ellipse. The point of orbit closest to Earth is called perigee, while the furthest point is known as apogee. The time taken from perigee to apogee and back to perigee is 28 days 13 hours 18 minutes and 33 seconds. Many specific phenomenons occur due to the difference in those two times.





