Vannamei shrimp is a promising commodity with a rapidly growing cultivation industry. Unfortunately, the industry is shadowed by the increasing threat of shrimp diseases. Common shrimp diseases include AHPND, EHP, WSSV, and IMNV. Early disease detection is crucial to anticipate the condition spread in shrimp ponds. Disease checking can be done before stocking or regularly throughout cultivation for monitoring.
One of the methods that can be used for disease checking in shrimp farms is through a PCR test. PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction, and relies on replicating DNA numerous times. PCR is a highly accurate test that can check for disease through pathogen DNA/RNA.
Here are three of the commonly used types of PCR for disease detection in shrimp:
- Conventional PCR
Conventional PCR is a qualitative PCR method that involves visualization through electrophoresis. The results obtained from conventional PCR are limited to positive and negative outcomes. The series of processes in conventional PCR include extraction, amplification, and electrophoresis. Electrophoresis is the process that sets conventional PCR apart from other PCR methods. This method serves as a reasonably accurate and relatively more affordable option for the detection of viral diseases compared to using a PCR Portable Kit.
- Real-Time PCR/qPCR
Real-time PCR is a PCR method that not only detects the presence of viral DNA but also determines the quantity of the virus in the tested sample. The concept of real-time PCR is similar to conventional PCR in DNA synthesis, but what sets it apart is that real-time PCR does not require the electrophoresis process, which can shorten the overall time. In real-time PCR, a fluorescent dye is used, allowing for the direct reading of the entire DNA amplification process. The use of real-time PCR enables accurate and rapid results, providing information on the quantity of the detected virus.
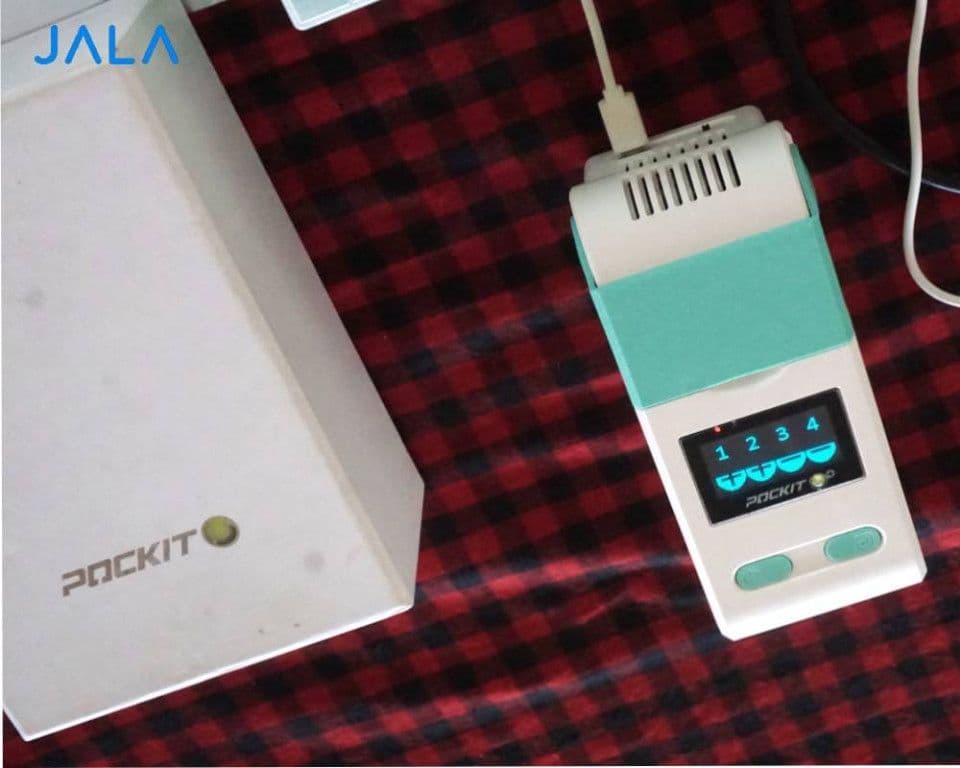
- iiPCR (Insulated Isothermal PCR)
In general, the principle of detection in iiPCR is similar to other PCR methods, with a different working mechanism. In iiPCR, the amplification of the target gene is carried out at a constant temperature, while in conventional PCR and real-time PCR, it is performed at three different temperatures in each cycle and repeated. The iiPCR process requires less time, and the results can be directly observed qualitatively (positive or negative) on the iiPCR machine or PCR Pockit display. iiPCR detects a positive result when the sample shows a signal of more than 10 copies of viral DNA.
PCR plays a crucial role in the shrimp farming industry for early detection of diseases in shrimp, thereby preventing and reducing losses caused by disease outbreaks. PCR facilities are currently available at the government's Balai Karantina Perikanan and Balai Budidaya Perikanan, as well as at feed laboratory facilities. Additionally, JALA also has PCR testing facilities using the iiPCR method located in Purworejo, Central Java.
Resources:
PCR – Polymerase Chain Reaction: Definition, Functions, Stages | Andaru PM
Fitri, Rr. Amaliah, Farida, dan Eko P. 2021. Perbandingan Metode PCR Konventional dengan Metode PCR Portable Kit untuk Deteksi WSSV Pada Udang Vannamei. Jurnal Ruaya. 9(1): 54-62